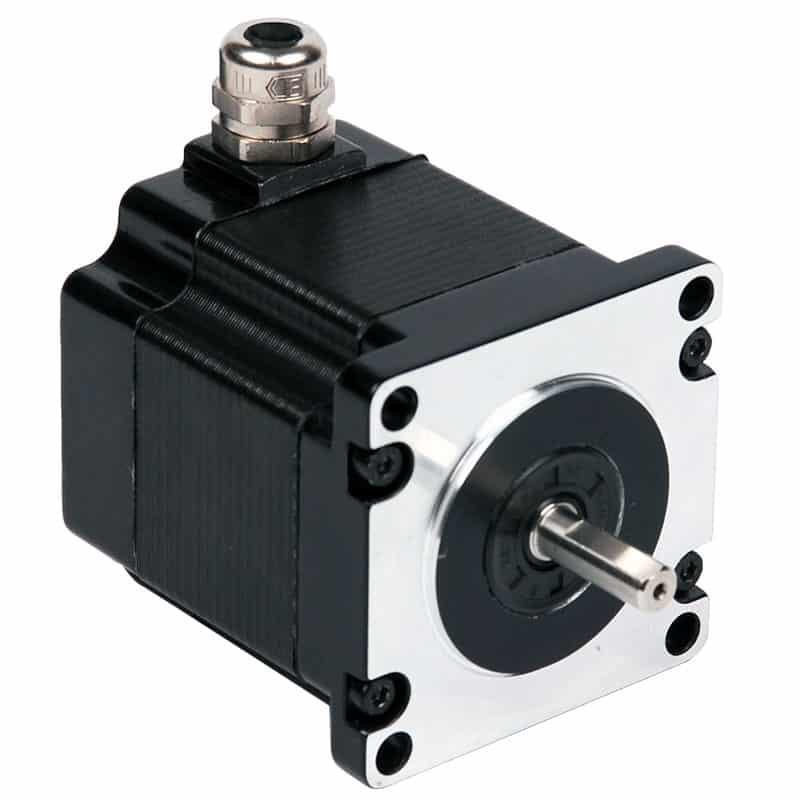
A stepper motor, also called a stepper, is a brushless synchronous electric motor. A stepper motor has the unique feature that a complete rotation is divided into a number of equal steps, where the angular distortion has a fixed value, for example 1.8 ° or 0.9 ° per step.
Stepper
Stepper motors deliver a relatively high torque at low rpm, even at total downtime. This is called the hold torque (holding torque) and with this the stepper motor can also be used as a brake in certain cases. All this makes stepper motors very suitable for positioning applications with low rpm and high torque. In addition, we can also apply a stepper motor in servo step mode, where we still maintain the aforementioned specific advantages, without loss of the increments also in the higher RPM range, lower temperature, et cetera.
Advantages
- High torque at low rpm
- Robust and reliable
- Easy to apply and manage
- Low-cost technology with huge potential
Disadvantages
- Low torque at high rpm
- Vibration, partly remedy by micro stepping
Variations & Features
- Hybrid stepper Motor; In principle equal to PM steppers, however, of better quality. Equipped with of better bearings, coils, etc., for higher power density and better positioning accuracy.
- PM Stepper Motor; This is a permanent magnet stepper motor, better known as ‘ tin-can ‘ steppers. Compact low-cost steppers with less power and lower accuracy.
- 3-Phase Stepper motor
- Various wrapping versions, and steering options, bipolar or unipolar
- Dimensions of NEMA8 upto NEMA42 and usually available in at least three different stack lengths.
- Open loop or closed loop control M.G.V. feedback systems.
- Step sizes of 0.9 °, 1.8 °, 7.5 ° and 15 °.
- Micro stepping for vibration suppression and fluid movements.
- Various IP classes up to IP67
Application Fields
- Pharmaceutical and medical sector
- Robotic
- Semiconductor, lithography and pick-and place systems
- Entertainment and digital signage, art and new media
- Horti-and agro-technology
- CNC, metal and woodworking
- Material Handling and packaging industry
- Chemical and petrochemical Industry